Build the Todo Application
Build the Todo Application
In this getting started exercise, you will create a simple Todo application using a CQRS design pattern that's backed by Apache Kafka and Zilla as the event-driven API gateway. Zilla lets you focus on your applications and business logic instead of spending time writing tons of code and this demo helps to ease CQRS complexity. This tutorial gives a basic introduction to Zilla and describes some straightforward capabilities.
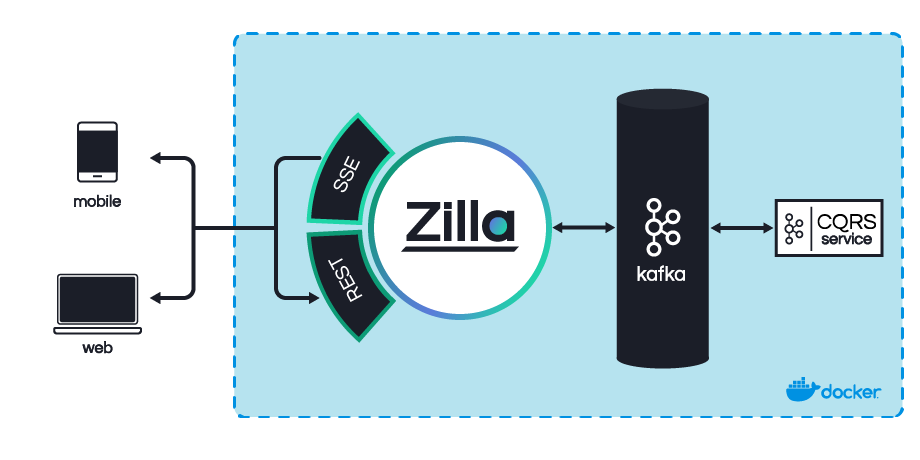
This Todo Application tutorial has the following goals:
- Provide a list of Todo tasks that is shared by all clients
- Support optimistic locking with conflict detection when attempting to update a Todo task
- Deliver updates in near real-time when a Todo task is created, modified, or deleted
- Demonstrate a user interface driving the Tasks API
- Support scaling Todo task reads and writes
Prerequisites
- Docker
20.10.14 - Git
2.32.0 - npm
8.3.1and above
Step 1: Kafka (or Redpanda)
In this step, you will set up basic infrastructure components for your event-driven architecture.
NOTE
Run docker swarm init if you already haven't done to initiateSwarm orchestrator.
Let's create stack.yml and add Apache Kafka (or Redpanda).
version: "3"
networks:
net:
driver: overlay
services:
kafka:
image: "bitnami/kafka:3.1.0"
hostname: "kafka.internal.net"
networks:
- net0
command:
- 'sh'
- '-c'
- '/opt/bitnami/scripts/kafka/setup.sh && kafka-storage.sh format --config "$${KAFKA_CONF_FILE}" --cluster-id "lkorDA4qT6W1K_dk0LHvtg" --ignore-formatted && /opt/bitnami/scripts/kafka/run.sh' # Kraft specific initialise
environment:
- ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER=yes
- KAFKA_CFG_NODE_ID=1
- KAFKA_CFG_BROKER_ID=1
- KAFKA_CFG_CONTROLLER_QUORUM_VOTERS=1@127.0.0.1:9093
- KAFKA_CFG_LISTENER_SECURITY_PROTOCOL_MAP=CLIENT:PLAINTEXT,INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT
- KAFKA_CFG_CONTROLLER_LISTENER_NAMES=CONTROLLER
- KAFKA_CFG_LOG_DIRS=/tmp/logs
- KAFKA_CFG_PROCESS_ROLES=broker,controller
- KAFKA_CFG_LISTENERS=CLIENT://:9092,INTERNAL://:29092,CONTROLLER://:9093
- KAFKA_CFG_INTER_BROKER_LISTENER_NAME=INTERNAL
- KAFKA_CFG_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS=CLIENT://localhost:9092,INTERNAL://kafka.internal.net:29092
ports:
- 9092:9092
init-topics:
image: "bitnami/kafka:3"
networks:
- net0
deploy:
restart_policy:
condition: none
max_attempts: 0
depends_on:
- kafka
entrypoint: [ '/bin/sh', '-c' ]
command: |
"
# blocks until Kafka becomes reachable
/opt/bitnami/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.internal.net:29092 --list --topic 'task-.*'
echo '## Creating the Kafka topics'
/opt/bitnami/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.internal.net:29092 --create --if-not-exists --topic task-commands --partitions 1
/opt/bitnami/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.internal.net:29092 --create --if-not-exists --topic task-replies --partitions 1
/opt/bitnami/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.internal.net:29092 --create --if-not-exists --topic task-snapshots --config cleanup.policy=compact --partitions 1
echo ''
echo '## Created the Kafka topics'
/opt/bitnami/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server kafka.internal.net:29092 --list --topic 'task-.*'
"
version: "3"
networks:
net:
driver: overlay
services:
redpanda:
image: 'docker.vectorized.io/vectorized/redpanda:v22.3.4'
hostname: "kafka.internal.net"
command:
- redpanda
- start
- '--smp'
- '1'
- '--reserve-memory'
- 0M
- '--overprovisioned'
- '--node-id'
- '0'
- '--kafka-addr'
- 'INSIDE://0.0.0.0:29092,OUTSIDE://0.0.0.0:9092'
- '--advertise-kafka-addr'
- 'INSIDE://redpanda:29092,OUTSIDE://localhost:9092'
networks:
- net0
ports:
- '9092:9092'
- '29092:29092'
- '9644:9644'
init-topics:
image: 'docker.vectorized.io/vectorized/redpanda:v22.3.4'
networks:
- net0
deploy:
restart_policy:
condition: none
max_attempts: 0
depends_on:
- redpanda
entrypoint: [ '/bin/sh', '-c' ]
command: |
"
# blocks until Redpanda becomes reachable
while ! rpk cluster status --brokers kafka.internal.net:29092
do
sleep 1
done
echo '## Creating the Redpanda topics'
rpk topic create --brokers kafka.internal.net:29092 --partitions 1 task-commands
rpk topic create --brokers kafka.internal.net:29092 --partitions 1 task-replies
rpk topic create --brokers kafka.internal.net:29092 --partitions 1 --config cleanup.policy=compact task-snapshots
echo ''
echo '## Created the Redpanda topics'
rpk topic list --brokers kafka.internal.net:29092 --regex 'task-.*'
"
Now let's run
docker stack deploy -c stack.yml example --resolve-image never
to spin up Apache Kafka (or Redpanda) and create the following topics.
task-commands | Queues commands to be processed by the Todo service |
task-replies | Queues the response from the Todo service after processing each command |
task-snapshots | Captures the latest snapshot of each task entity |
Now verify that the Kafka topics have been successfully created.
docker service logs example_init-topics --follow --raw
Make sure you see this output at the end of the example_init-topics service logs.
## Creating the Kafka topics
Created topic task-commands.
Created topic task-replies.
Created topic task-snapshots.
## Created the Kafka topics
task-commands
task-replies
task-snapshots
CLUSTER
=======
redpanda.initializing
BROKERS
=======
ID HOST PORT
0* redpanda 29092
## Creating the Redpanda topics
TOPIC STATUS
task-commands OK
TOPIC STATUS
task-replies OK
TOPIC STATUS
task-snapshots OK
## Created the Redpanda topics
NAME PARTITIONS REPLICAS
task-commands 1 1
task-replies 1 1
task-snapshots 1 1
Step 2: Todo Service
Next, you will need to build a todo service that is implemented using Spring boot + Kafka Streams to process commands and generate relevant output. This Todo service can deliver near real-time updates when a Task is created, renamed, or deleted, and produces a message to the Kafka task-snapshots topic with the updated value.
Combining this with cleanup-policy: compact for the task-snapshots topic causes the topic to behave more like a table, where only the most recent message for each distinct message key is retained.
This approach is used as the source of truth for the current state of our Todo service, setting the Kafka message key to the Task identifier to retain all the distinct Tasks.
When a Task is deleted, you will produce a tombstone message (null value) to the task-snapshots topic causing that Task identifier to no longer be retained in Kafka.
Commands arrive at the Tasks service via the task-commands topic and correlated replies are sent to the task-replies topic with the same zilla:correlation-id value that was received with the inbound command message.
Implementing the Todo domain using these topics gives us the following Kafka Streams topology.
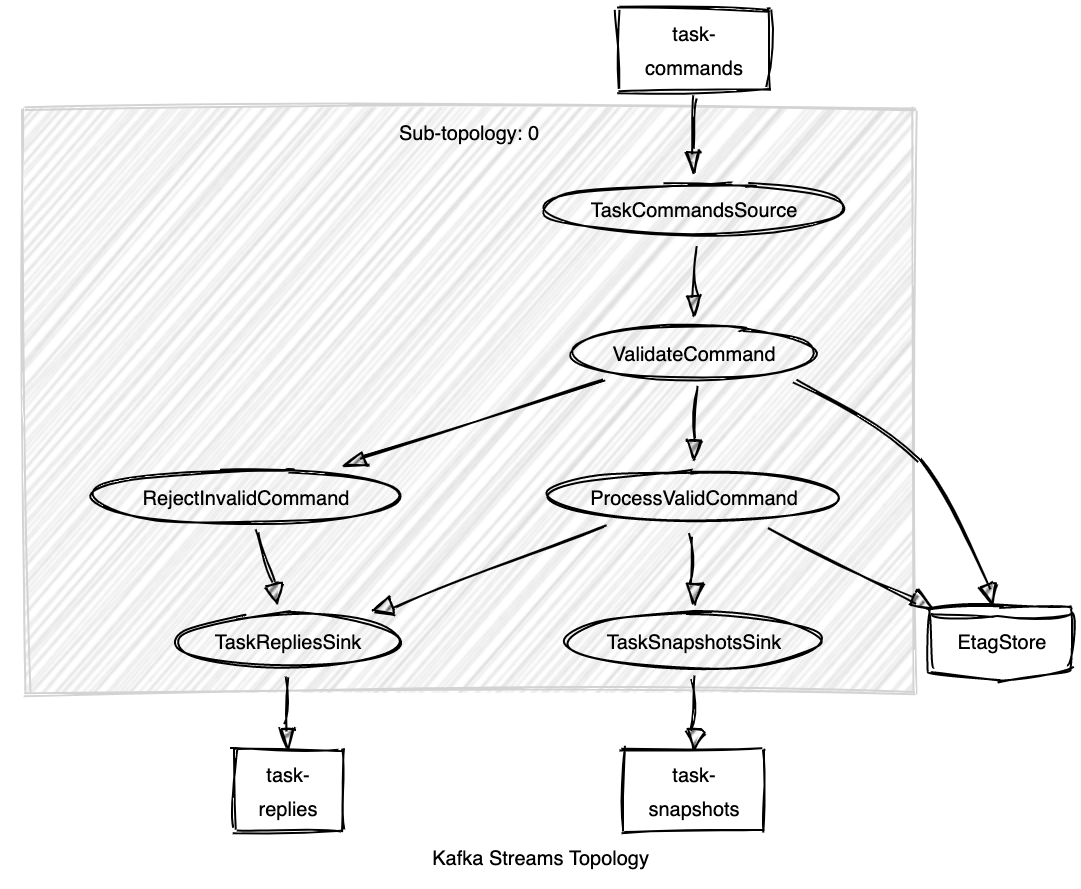
The ValidateCommand Kafka Streams processor implements optimistic locking by ensuring that conditional requests using if-match are allowed to proceed only if the latest etag for the Task matches, otherwise the command is rejected.
Let's checkout and build the service by running the commands below.
git clone https://github.com/aklivity/todo-service && \
cd todo-service && \
./mvnw clean install && \
cd ..
This will checkout and build todo-service:latest image.
Open stack.yml file and add the Todo service into the stack:
...
todo-service:
image: "todo-service:latest"
networks:
- net0
environment:
SPRING_KAFKA_APPLICATION_ID: todo-service
SPRING_KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS: kafka.internal.net:29092
TASK_COMMANDS_TOPIC: task-commands
TASK_SNAPSHOTS_TOPIC: task-snapshots
TASK_REPLIES_TOPIC: task-replies
Run the command below to deploy the todo-service to your existing stack.
docker stack deploy -c stack.yml example --resolve-image never
Creating service example_todo-service
Updating service example_kafka (id: st4hq1bwjsom5r0jxnc6i9rgr)
Creating service example_todo-service
Updating service example_redpanda (id: ilmfqpwf35b7ftd6cvzdis8au)
Now, you have a running to-do service that can process incoming commands, send a response and take snapshots of the task.
Step 3: Zilla
Next, the most exciting and most challenging part of implementing the CQRS design pattern is where you need to build and deploy your API with a real-time response.
In a traditional approach, you would have to set up and build multiple layers of service implementation to expose the API that is based on Kafka Streams.
However, Zilla is designed to solve these architectural challenges, requiring only declarative configuration as shown below.
Let's design the Tasks API. You need to define a Tasks API to send commands to the Todo service via Kafka and retrieve task queries from Kafka as needed by the Tasks UX.

Details
Creates a new Todo Task.
Requires content-type application/json and request body matching CreateTask command domain model.
Include idempotency-key of type uuid to support idempotent CreateTask.
Responses:
201: Created - Task created successfully

Details
Rename Task
Renames a Todo Task.
Requires content-type application/json and request body matching RenameTask command domain model.
Include idempotency-key of type uuid to support idempotent RenameTask.
Include if-match with current etag to provide optimistic locking.
Parameters
Path:
id[String] - Task identifier
Header:
if-match[String] - Task etag
Responses:
- 204 No Content - Task renamed successfully
- 412 Precondition Failed - Task rename failed, etag does not match

Details
Delete Task
Requires content-type application/json and request body matching DeleteTask command domain model.
Include idempotency-key of type uuid to support idempotent DeleteTask.
Include if-match with current etag to provide optimistic locking.
Parameters
Path:
id[String] - Task identifier
Header:
if-match[String] - Task etag
Responses:
- 204 No Content - **** Task deleted successfully
- 412 Precondition Failed - **** Task delete failed, etag does not match

Details
Get Tasks
Retrieves all tasks, with etag representing the **** latest value.
Parameters
Header:
if-none-match[String] - Tasks collection etag
Responses:
- 200 OK - Returns an array of Tasks
- 304 Not Modified - **** If Tasks collection etag matches
Configure Zilla
The Zilla engine configuration defines a flow of named bindings representing each step in the pipeline as inbound network traffic is decoded and transformed then encoded into outbound network traffic as needed.
Let's configure Zilla for the Tasks API to interact with the Todo Kafka Streams service via Kafka topics.
You will add the following bindings to support the Tasks API as shown zilla.yaml below. To understand each binding type in more detail please visit Zilla Runtime Configuration.
tcp_server | listens on port 8080 routes to http_server |
http_server | decodes HTTP protocol routes Tasks API to http_kafka_proxy |
http_kafka_proxy | transforms HTTP to Kafka routes POST, PUT and DELETE Tasks API requests to task-commands topic with task-replies reply-to topic via kafka_cache_client routes GET Tasks API requests to task-snapshots topic via kafka_cache_client |
kafka_cache_client | reads from local Kafka topic message cache routes to kafka_cache_server |
kafka_cache_server | writes to local Kafka topic message cache as new messages arrive from Kafka routes to kafka_client |
kafka_client | encodes Kafka protocol routes to kafka_client |
tcp_client | connects to Kafka brokers |
Using Zilla Studio, select the Build the Todo App template from the Load Template dropdown and then press Generate Config to download the corresponding zilla.yaml configuration file.

Alternatively, copy the contents of zilla.yaml shown below to your local zilla.yaml file.
zilla.yaml
name: Example
vaults: {}
bindings:
tcp_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: tcp
kind: server
options:
host: 0.0.0.0
port: 8080
exit: http_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
http_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: http
kind: server
options:
access-control:
policy: cross-origin
routes:
- when:
- headers:
:method: GET
:path: /tasks
exit: sse_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
- when:
- headers:
:method: POST
:path: /tasks
- headers:
:method: PUT
:path: /tasks/*
- headers:
:method: DELETE
:path: /tasks/*
exit: http-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
sse_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: sse
kind: server
exit: sse-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
sse-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: sse-kafka
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- path: /tasks
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
event:
id: '["${base64(key)}","${etag}"]'
topic: task-snapshots
http-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: http-kafka
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- method: POST
path: /tasks
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${idempotencyKey}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: CreateTaskCommand
- when:
- method: PUT
path: /tasks/{id}
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${params.id}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: RenameTaskCommand
- when:
- method: DELETE
path: /tasks/{id}
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${params.id}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: DeleteTaskCommand
kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: cache_client
exit: kafka_cache_serverda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
kafka_cache_serverda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: cache_server
options:
bootstrap:
- task-replies
- task-snapshots
exit: kafka_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
kafka_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: client
exit: tcp_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
tcp_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: tcp
kind: client
options:
host: kafka.internal.net
port: 29092
routes:
- when:
- cidr: 0.0.0.0/0
guards: {}
Now let's add the zilla service to the docker stack, mounting the zilla.yaml configuration.
...
zilla:
image: "ghcr.io/aklivity/zilla:latest"
hostname: "zilla"
command: ["start", "-v", "-e"]
volumes:
- ./zilla.yaml:/etc/zilla/zilla.yaml:ro
networks:
- net0
ports:
- "8080:8080"
...
Run the below command as this will deploy the zilla service to the existing stack.
docker stack deploy -c stack.yml example --resolve-image never
Updating service example_kafka (id: st4hq1bwjsom5r0jxnc6i9rgr)
Updating service example_todo-service (id: ojbj2kbuft22egy854xqv8yo8)
Creating service example_zilla
Updating service example_redpanda (id: ilmfqpwf35b7ftd6cvzdis8au)
Updating service example_todo-service (id: 1tq9nktlvcwxeh3wzhmj02cvd)
Creating service example_zilla
NOTE
Make sure that Zilla is fully started by checking container logs where you see started at the end of the log.
Let's verify the Tasks API using the curl POST and GET commands shown below.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/tasks \
-H "Idempotency-Key: 5958F9A2-8319-486B-BD43-2F80FDE87223" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{\"name\":\"Read the docs\"}"
curl http://localhost:8080/tasks
id:["NTk1OEY5QTItODMxOS00ODZCLUJENDMtMkY4MEZERTg3MjIz","AQIAAg==/1"]
data:{"name":"Read the docs"}
As you can see, the GET /tasks API delivers a continuous stream of tasks starting with the initial tasks as expected.
Now create a new Todo task while keeping the GET /tasks stream open as shown above.
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/tasks \
-H "Idempotency-Key: 5C1A90A3-AEB5-496F-BA00-42D1D805B21B" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d "{\"name\":\"Join the Slack community\"}"
The GET /tasks stream automatically receives the update when the new task is created.
id:["NUMxQTkwQTMtQUVCNS00OTZGLUJBMDAtNDJEMUQ4MDVCMjFC","AQIABA==/1"]
data:{"name":"Join the Slack community"}
Each new update arrives automatically, even when changes are made by other clients.
Step 4: Web App
Next, you will build the Todo app that's implemented using VueJs framework. Run the commands below in the root directory.
git clone https://github.com/aklivity/todo-app && \
cd todo-app && \
nvm install && nvm use \
npm install && \
npm run build && \
cd ..
This will generate dist folder with necessary artifacts. Now you can configure Zilla to host the app so that both API and app can be served under the same hostname and port.
First, add the http_filesystem_proxy and filesystem_server bindings to zilla.yaml giving the following updated configuration.
zilla.yaml (updated)
name: Example
vaults: {}
bindings:
tcp_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: tcp
kind: server
options:
host: 0.0.0.0
port: 8080
exit: http_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
http_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: http
kind: server
options:
access-control:
policy: cross-origin
routes:
- when:
- headers:
:method: GET
:path: /tasks
exit: sse_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
- when:
- headers:
:method: POST
:path: /tasks
- headers:
:method: PUT
:path: /tasks/*
- headers:
:method: DELETE
:path: /tasks/*
exit: http-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
exit: http_filesystem_proxy
sse_serverab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: sse
kind: server
exit: sse-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800
sse-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: sse-kafka
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- path: /tasks
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
event:
id: '["${base64(key)}","${etag}"]'
topic: task-snapshots
http-kafka_proxyab9279f6-00aa-40a9-b10a-268c5ebfd800:
type: http-kafka
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- method: POST
path: /tasks
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${idempotencyKey}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: CreateTaskCommand
- when:
- method: PUT
path: /tasks/{id}
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${params.id}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: RenameTaskCommand
- when:
- method: DELETE
path: /tasks/{id}
exit: kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
with:
capability: produce
reply-to: task-replies
topic: task-commands
key: ${params.id}
overrides:
zilla:domain-model: DeleteTaskCommand
kafka_cache_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: cache_client
exit: kafka_cache_serverda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
kafka_cache_serverda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: cache_server
options:
bootstrap:
- task-replies
- task-snapshots
exit: kafka_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
kafka_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: kafka
kind: client
exit: tcp_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c
tcp_clientda6b9d8f-0846-4b2b-8ed6-b8db5605e50c:
type: tcp
kind: client
options:
host: kafka.internal.net
port: 29092
routes:
- when:
- cidr: 0.0.0.0/0
http_filesystem_proxy:
type: http-filesystem
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- path: /
exit: filesystem_server
with:
path: index.html
- when:
- path: /{path}
exit: filesystem_server
with:
path: ${params.path}
filesystem_server:
type: filesystem
kind: server
options:
location: /app/dist/
guards: {}
The last step is to mount the dist folder into the Zilla container.
Open stack.yml file and add - ./todo-app/dist:/app/dist:ro to the zilla service volumes.
stack.yml
...
zilla:
image: "ghcr.io/aklivity/zilla:latest"
hostname: "zilla"
command: ["start", "-v", "-e"]
volumes:
...
- ./todo-app/dist:/app/dist:ro
...
Finally, run
docker stack deploy -c stack.yml example --resolve-image never
Make sure that zilla.yaml config changes got applied after restarting the Zilla service. Check the example_zilla service log.
Step 5: Test Drive
Open the browser and enter http://localhost:8080/ to see the Todo Application.

Notice that there is no need to Login as the Tasks API is initially available to anonymous clients.
Next up: Secure the Todo Application Tasks API with JWT access tokens.

